Judicial Reform in China
JUDICIAL REFORM IN CHINA
Information Office of the State Council
The People’s Republic of China
October 2012, Beijing
Contents
Preface
I. Judicial System and Reform Process
II. Maintaining Social Fairness and Justice
III. Strengthening Human Rights Protection
IV. Enhancing Judicial Capabilities
V. Judicial Power Serving the People
Conclusion
Preface
The judicial system is a major component of the political system, while judicial impartiality is a significant guarantee of social justice.
Since the founding of New China in 1949, and especially since the reform and opening-up policies were introduced some three decades ago, China, proceeding from its national conditions, carrying on the achievements of Chinese traditional legal culture and learning from other civilizations regarding their rule of law, has been building and improving its socialist judicial system with Chinese characteristics, safeguarding social justice and making significant contributions to the rule of law of the mankind.
China’s judicial system is generally consistent with its basic national conditions at the primary stage of socialism, its state system of people’s democratic dictatorship, and its government system of the National People’s Congress. With the further development of China’s reform and opening up, particularly due to the development of the socialist market economy, the comprehensive implementation of the fundamental principle of rule of law, and the increasing demands of the public for justice, China’s judicial system urgently needs to be reformed, improved and developed.
In recent years, China has been promoting the reform of the judicial system and its work mechanism vigorously, steadily and pragmatically. Aiming to safeguard judicial justice and focusing on optimizing the allocation of judicial functions and power, enhancing protection of human rights, improving judicial capacity, and practicing the principle of “judicature for the people,” China has been striving to improve its judicial system with Chinese characteristics, expand judicial democracy, promote judicial openness and ensure judicial impartiality. This provides a solid judicial guarantee for China’s economic development, social harmony and national stability.
I. Judicial System and Reform Process
The founding of the People’s Republic of China in 1949 ushered in a new era for the building of China’s judicial system. The Common Program of the Chinese People’s Political Consultative Conference, which functioned as a provisional Constitution, and the Organic Law of the Central People’s Government of the People’s Republic of China, both promulgated in September 1949, laid the cornerstone for legal construction in New China. The Constitution of the People’s Republic of China promulgated in 1954, the Organic Law of the People’s Courts of the People’s Republic of China, the Organic Law of the People’s Procuratorates of the People’s Republic of China among other laws and regulations, defined the organic system and basic functions of the people’s courts and procuratorates, established the systems of collegiate panels, defense, public trial, people’s jurors, legal supervision, civil mediation, putting into place the basic framework of China’s judicial system.
Toward the end of 1950s, especially during the ten-year tumultuous “cultural revolution” (1966-1976), China’s judicial system suffered severe damage. Since the reform and opening-up policies were introduced in 1978, China, after summing up its historical experience, established the fundamental policy of promoting socialist democracy and improving socialist legal construction, restored and rebuilt the judicial system, and formulated and amended a range of fundamental laws. In the 1990s, China established the fundamental principle of governing the country in accordance with the law, and quickened the step to build China into a socialist country under the rule of law. During the process of promoting social progress, democracy and the rule of law, China’s judicial system is continuously improving and developing.
1. Basic Characteristics of China’s Judicial System
China is a socialist country with a people’s democratic dictatorship led by the working class and based on the alliance of workers and peasants. The people’s congress system is the organic form of its state power. China’s state system and system of government decide that its judicial power comes from the people, belongs to the people and serves the people. The people’s courts and the people’s procuratorates are created by the people’s congresses at various levels, to which they are responsible and by which they are supervised.
The people’s court is the basic judicial organ in China. The state has set up the Supreme People’s Court, local people’s courts at different levels and special people’s courts such as military courts. They adjudicate civil, criminal and administrative cases in accordance with the law, and carry out law enforcement activities including the execution of civil and administrative cases and state compensation. The Supreme People’s Court supervises the judicial work of all local people’s courts and special people’s courts. The people’s court at a higher level supervises the judicial work of the people’s court at the next lower level. In litigious activities, China adopts the systems of public trial, collegiate panels, challenge, people’s jurors, defense, and judgment of the second instance as final, among others.
The people’s procuratorate is the procuratorial organ in China. The state has set up the Supreme People’s Procuratorate, local people’s procuratorates at different levels and special people’s procuratorates such as military procuratorates. The Supreme People’s Procuratorate directs the work of local people’s procuratorates at different levels and special people’s procuratorates. A people’s procuratorate at a higher level directs the work of a people’s procuratorate at the next level below it. The people’s procuratorate exercises legal supervision over criminal, civil and administrative litigations in accordance with the law.
The people’s court and the people’s procuratorate exercise their adjudicative power and procuratorial power independently and impartially in accordance with the law. Their exercise of power is subject to the supervision of the National People’s Congress, the Chinese People’ s Political Consultative Conference and the general public.
The people’s courts, the people’s procuratorates and the organs of public security handle criminal cases according to their respective functions, and collaborate with and check each other, so as to ensure the accurate and efficient implementation of law. The organs of public security take charge of the investigation, detention, arrest and pretrial in criminal cases; the people’s procuratorates conduct procuratorial work, approve proposals for arrest, investigate cases directly accepted by them, and initiate public prosecution; and the people’s courts are responsible for conducting trials.
2. Objectives, Principles and Process of China’s Judicial Reform
Since the introduction of the reform and opening-up policies, China has witnessed rapid economic and social development, and the public’s awareness of the importance of the rule of law has been remarkably enhanced. Due to the profound changes in the judicial environment, judicial work in China is facing new situations and problems. The defects and rigidity in China’s current judicial system and its work mechanism are becoming increasingly prominent, and they need to be improved gradually through reform.
The fundamental objectives of China’s judicial reform are to ensure that the people’s courts and people’s procuratorates exercise adjudicative power and procuratorial power fairly and independently; to establish an impartial, efficient and authoritative socialist judicial system; and to provide solid and reliable judicial guarantee for safeguarding the legitimate rights and interests of the people, social equity and justice, and lasting national stability.
China carries out judicial reform based on its national conditions. It draws on the sound practices of other countries but does not blindly copy them; it keeps pace with the times but does not advance rashly and blindly. It sticks to the line of relying on the people, strives to meet their expectations, tackles problems of particular concern to the people, and subjects itself to their supervision and examination, so as to ensure the reform is for the people, relies on the people and benefits the people. It pushes forward the reform in accordance with the law, abiding by the Constitution and other laws and regulations, while those measures that contravene the laws in force should only be implemented after the laws are revised. It adheres to the principle of overall planning and coordination, comprehensive designing, and proceeding in an orderly and gradual way.
As early as in the 1980s, China started reforms in court trials and ensuring professionalism in judicature, focusing on enhancing the function of court trials, expanding the openness of trials, improving attorney defense functions, and training professional judges and procurators.
In 2004, China launched large-scale judicial reforms based on overall planning, deployment and implementation. Starting with issues that caused complaints from the public and the key links that hamper judicial justice, according to the demands of promoting judicial impartiality and strict enforcement of the law, and proceeding from the regular pattern and characteristics of judicial practice, China improved the structure of its judicial organs, division of judicial functions and system of judicial management, to establish a judicial system featuring clearly defined power and responsibilities, mutual collaboration and restraint, and highly efficient operation. Thereby, China’s judicial reform entered a phase of overall planning and advancing in an orderly way.
Since 2008, China has initiated a new round of judicial reform, and entered a stage of deepening in key areas and overall advancement. The reform proceeds from the demands of the public for justice, with safeguarding the people’s common interests as its fundamental task, promoting social harmony as the main principle and strengthening supervision and restraint of power as priority. China aims to tackle problems in the key links that hamper judicial justice and restrain judicial capability, remove existing barriers in the institutional setup and operational mechanism as well as provision of legal guarantee, and put forward the specific tasks for judicial reform in four aspects - optimizing the allocation of judicial functions and power, implementing the policy of balancing leniency and severity, building up the ranks of judicial workers, and ensuring judicial funding. Currently, the tasks of this round of judicial reform have been basically completed, as relevant laws have been amended and improved. As China is making continuous progress in economic and social development, its judicial reform is bound to advance further.
II. Maintaining Social Fairness and Justice
Maintaining social fairness and justice is the value to be enforced in China’s judicial reform. China aims its judicial reform at strengthening its judicial organs’ capability in maintaining social justice by optimizing the structure of the judicial organs and allocation of their functions and power, standardizing judicial acts, improving judicial proceedings, and enhancing judicial democracy and legal supervision.
1. Optimizing the Allocation of Judicial Functions and Power
The rationalization and optimization of judicial functions and power has a direct bearing on the materialization of justice. China, starting from removing the institutional barriers that affect judicial impartiality, has enhanced internal checks in judicial organs, clarified the work relationship between the people’s courts and the people’s procuratorates at different levels, standardized and improved retrial procedures, and established consistent law-enforcement system and judicial authentication management system. These reforms have improved judicial organs’ capacity for maintaining fairness, helped to safeguard social equity and justice, and fulfilled the public’s new expectations and demands for the judicial system in maintaining justice.
Separation of filing, trial and execution of cases. The people’s courts at all levels have established case-filing tribunals, execution bureaus and other departments in addition to the original criminal, civil and administrative adjudication tribunals. Case-filing, trial and execution are handled separately by different offices, which act independently and exercise a mutual-check function to ensure the fair exercise of adjudicative and execution power.
Standardizing the retrial of remanded cases and designated cases. To correct the irregular practices in the procedures regarding retrial of remanded cases and designated cases, the Civil Procedure Law amended in 2012 revised and improved the procedure for the retrial of remanded cases. The new provisions clearly state that after the original people’s court makes its ruling in the retrial of a remanded case, if the litigant makes an appeal, the people’s court of second instance shall not send the case back for a retrial. The Criminal Procedure Law, amended in 2012, articulates that a criminal case designated for retrial by a lower-level people’s court shall be tried by one other than the original court in principle.
Regularizing and improving a unified execution mechanism for civil and administrative cases. Full and effective execution of a judgment or verdict given by the court bears on effective protection of the lawful rights of all parties involved and the expression of judicial authority. In recent years, local people’s courts have established a mechanism of execution that works closely with departments in charge of public security, procuratorial work, finance, land resources, construction, business and commerce, as well as exit-entry administration. The people’s courts exercise separation of jurisdiction from execution. The higher and intermediate people’s courts have established execution command centers for unified management and coordination of execution, and, when necessary, can have their power elevated or allow them to carry out the execution beyond the prescribed region. The reform of the execution system has further strengthened the internal checks on the exercise of execution power, promoted impartial and standardized execution, and effectively protected the legitimate rights of the parties concerned.
Reforming the procedures for examining and approving arrests in power-abuse cases. To prevent arrests by mistake, China has reformed the procedure for examining and approving arrests in power-abuse cases. For power-abuse cases filed with and investigated by a people’s procuratorate below the provincial level, the approval for an arrest shall be examined and determined by the people’s procuratorate at the next higher level. This reform has strengthened the supervision of a people’s procuratorate at a higher level over one at a lower level on law enforcement.
Improving the system of judicial authentication management. Judicial authentication refers to the activity of an authenticator applying scientific technology or specialized knowledge to identify and determine the specialized issues involved in a lawsuit and giving authentication opinions. Before the judicial reform, the judicial authentication system in China had problems as legislation was incomplete, management was not standardized and standards were not consistent. To solve these problems, China’s legislative organ promulgated the Decision on the Management of Judicial Authentication in 2005, thereby establishing a uniform management and registration system for judicial authentication. The judicial administrative departments of the State Council take charge of the registration and management of judicial authenticators and judicial authentication institutions in China, while the judicial administrative departments of the people’s governments at the provincial level are responsible for the registration upon examination, roster formulation and roster announcement of judicial authenticators and judicial authentication institutions. The people’s courts and judicial administrative departments do not have judicial authentication institutions any longer; judicial authentication institutions already set up by investigation organs to meet the needs of their work will not provide judicial authentication services to the public. The state promotes a mechanism that combines administrative management with trade associations’ self-disciplinary management, and adopts the system of judicial authenticators’ independent practice in accordance with the law, which ensures that judicial authentication is standardized and neutral. By the end of 2011, there were 5,014 judicial authentication institutions and 52,812 judicial authenticators approved and registered in China.
2. Standardizing Judicial Acts
Social fairness and justice shall be ensured in the trial of every case and in each judicial act. Due to the country’s unbalanced economic and social development, different law-enforcement capabilities of judicial personnel and remnants of local protectionism, there are still problems like non-transparent exercise of judicial discretion and non-standardized judicial acts. In recent years, China’s judicial organs have vigorously pushed forward the standardization of penalties, established the case guidance system, and enhanced case management, all of which have promoted standardization of judicial acts.
Standardizing penalties. To regulate acts in giving out a sentence, the Supreme People’s Court, by summarizing pilot experiences, has formulated the Guiding Opinions on Sentencing by the People’s Courts (Trial Implementation) and Opinions on Several Issues Concerning the Regulation of Sentencing Procedures (Trial Implementation). Both documents clarify the sentencing processes, subdivide the range of statutory sentencing and clarify the quantification standards for different circumstances when giving out a sentence. For cases of public prosecution, the people’s procuratorate provides suggestions on sentencing in accordance with the law, while the litigant, the defender and the procurator may give opinions on the penalty. Comparatively independent sentencing procedures have been established for court trials, so as to facilitate investigations and debates over the facts and evidence concerning conviction and sentencing in a case. The people’s courts should explain the reasons for sentencing in their documents of criminal judgment. These reforms have further standardized sentencing jurisdiction, and maintained transparency and impartiality of sentencing.
Establishing the case guidance system. In 2010, China’s judicial organs issued regulations on building a case guidance system, marking the establishment of a case guidance system with Chinese characteristics. Different from the system of case judgment in the common law, China’s case guidance system - under the statutory law - uses cases to give directions for the accurate understanding and appropriate application of the provisions of laws. In recent years, judicial organs have made public cases that are typical in the application of laws as guiding cases and references for judicial personnel at all levels to settle similar cases. The case guidance system has improved the standardized exercise of judicial discretion, and enhanced uniformity in the application of the law.
Enhancing case management. The people’s courts and people’s procuratorates have set up special case management institutions to improve the management of case-handling procedures and quality. By the end of May, 2012, nearly 1,400 people’s courts had set up special trial management institutions, and nearly 1,600 people’s procuratorates had set up special case management institutions. Public security organs have arranged for full-time/part-time legal personnel at the basic-level law enforcement organs to supervise and examine the process of case handling. Judicial organs have widely established information platforms for case management, which have realized online case handling, supervision and appraisal, and improved the level of standardized case handling.
3. Expanding Judicial Openness
In view of multiple social conflicts, large numbers of cases, and newly emerging problems and situations, China’s judicial organs, while building up their judicial capacity, are comprehensively promoting judicial openness, so as to ensure that judicial power is exercised openly, fairly and impartially under the supervision of all the people.
Expanding the items and content of judicial openness. People’s courts extend judicial openness in court trial to all other processes such as case-filing, execution, hearing, issue of documents, and jurisdiction affairs. The people’s procuratorates make fully public case-handling procedures, case review procedures, litigation participators’ rights, interests and obligations, and results of legal supervision in accordance with the law. Public security and judicial administration organs make known to the public their main functions and responsibilities, the basis, procedures and results of law enforcement, and discipline in the case of police affairs.
Diversifying the forms and carriers of judicial information disclosure. The form of judicial openness has been changed from separate information release by each judicial department to unified information disclosure through a designated information service platform. The carriers of judicial information disclosure have been extended from the traditional public notice boards, newspapers, periodicals and pamphlets, to websites, blogs, microblogs, instant communication tools, and other newly emerging online media. A press spokesman news briefing mechanism has been established and improved for timely judicial information release.
Enhancing the effectiveness of and guarantee for judicial openness. The reasoning and argumentation of all documents in relation to judgments, procuratorial work and public security affairs will be strengthened. Ordinary people and experts are invited to attend hearings and arguments. Email boxes are opened as a means of communication with the people and hotlines of the same number across the country are created for people to report offences. There are designated days when heads of judicial departments meet with visitors. The state has strengthened the manpower and material guarantees for judicial openness. All these measures have ensured that judicial openness advances in an orderly way and achieves positive results.
4. Enhancing Judicial Democracy
The people’s courts as the judicial organs and the people’s procuratorates as the legal supervisory organs also need to promote democracy to ensure judicial impartiality. China is striving to establish and improve the systems of people’s jurors and people’s supervisors. This provides a significant guarantee for developing socialist democratic politics, and realizing the people’s participation in the administration of state affairs in accordance with the law.
Improving the system of people’s jurors. The system of people’s jurors is a major way for the public to directly participate in and supervise judicial work. In 2004, China’s legislative organ promulgated the Decision on Improving the System of People’s Jurors. The state has expanded the sources of people’s jurors to all walks of life, and determine the people’s jurors for cases by random selection from the rosters. In a collegiate panel, people’s jurors have the same power as the judges, except that they cannot serve as chief judges, and exercise the right to vote independently for the findings of fact and the application of law. The people’s courts at all levels have held training sessions for people’s jurors, mainly focusing on judicial procedure, professional skills and awareness of the rule of law, so as to improve their capability to perform their duties.

The graphics shows cases with the Participation of People's Jurors from 2006 to 2011, according to China's white paper on judicial reform published by the Information Office of the State Council on Oct. 9, 2012.
Attempt to establish the system of people’s supervisors. In 2003, the Supreme People’s Procuratorate launched a pilot program to establish the system of people’s supervisors. In October 2010, this system is comprehensively implemented in procuratorial organs throughout the country. People’s supervisors are selected from all walks of life who supervise and assess, according to supervisory procedures, the following situations in power-abuse cases handled by the people’s procuratorates: failure in putting a case on file for investigation, wrongfully putting a case on file for investigation, and withdrawing a case or stopping prosecution. From October 2003 to the end of 2011, people’s supervisors in China supervised 35,514 cases, and gave opinions different from the original ones of the people’s procuratorates in 1,653 cases. People’s supervisors’ votes in 908 cases were adopted by the people’s procuratorates, accounting for 54.93% of the total.
5. Strengthening Legal Supervision by Procuratorial Organs
The people’s procuratorates exercise legal supervision over judicial activities, such as investigation, trial and execution. China sets enhancing supervision over judicial power as the focus of its judicial reform, and has taken a range of measures to strengthen legal supervision.
Strengthening legal supervision over case-filing and activities of the investigation organs. The people’s procuratorates and organs of public security have established a briefing system and information-sharing platform for criminal cases. By means of examining and approving for arrest, handling people’s petitions and visits, complaints of litigants, public opinion and media reports, the people’s procuratorates and organs of public security can promptly find clues to failures in putting a case on file for investigation, or wrongfully putting a case on file for investigation, so that they can review and deal with such situations in accordance with the law. When accepting a case, a charge or a reported offence, or discovering that investigation personnel have collected evidence illegally, the people’s procuratorates give suggestions for correction based on investigation and affirmation, and in the meantime, enhance supervision over the examination and approval of an arrest, the extension or recalculation of an investigation or detention. In 2011, the procuratorial organs in China supervised the filing of 19,786 cases. They urged the correction of unlawful procedures during the investigation of 39,432 cases.
Strengthening legal supervision over the judicial activities of the people’s courts. For criminal, civil and administrative judgments, rulings and mediation decisions that have come into effect, if mistakes are found in them or which might damage the national or public interest, or contravene legal procedures and affect judicial justice, the procuratorial organs are entitled to lodge a protest or give procuratorial suggestions and take other supervisory measures. The people’s courts shall deal with the matter and give a written reply within a month after receiving the procuratorial suggestion.
Strengthening legal supervision over penalty execution and surveillance and control process. In view of the exposure of some pernicious incidents in detention houses and prisons in recent years, the procuratorial organs, along with related departments, have launched a campaign to review law-enforcement work in detention houses and to “remove hidden dangers of accidents and promote safe custody” in prisons, in order to ensure the implementation of surveillance and control according to law. The procuratorial organs have intensified supervision over prison and other places of surveillance by regulating and strengthening the work on resident procurator’s offices established at these places, building up a network to share information on law enforcement and monitoring in these places, and improving and implementing mechanisms for supervision over detention procedures and for on-site inspections. In addition, the procuratorial organs have intensified supervision over commutation of punishment, parole and temporary execution of sentences outside prison, worked to establish a supervision mechanism for the punctual implementation of penalty changes, and conducted special checks on the implementation of medical parole and the use of enforcement tools and punishing confinement at detention houses. The newly amended Criminal Procedure Law promulgated in 2012 stipulates that prisons, detention houses and other surveillance agencies, when giving suggestions or written proposals to the people’s courts for commutation of punishment, release on parole or execution of sentence outside prison, should send the written proposals or copies of them to the people’s procuratorates, which can submit their opinions to the people’s courts in writing.
Strengthening supervision over judicial functionaries’ acts of dereliction of duty. The Supreme People’s Procuratorate, together with the Supreme People’s Court and other relevant organs, have formulated Some Regulations on Intensifying Legal Supervision over Judicial Functionaries’ Dereliction of Duty in Litigation Activities. It makes clear that procuratorial organs can exercise their supervision over 12 acts of dereliction of duty (including bending the law for personal gains) on the part of judicial functionaries by investigating and confirming the alleged violations, giving rectification opinions, and suggesting that the judicial functionaries in question be replaced, in order to punish dereliction of duty, to curb judicial corruption and safeguard justice.
III. Strengthening Human Rights Protection
To strengthen the protection of human rights is an important goal of China’s judicial reform. China’s legislative body promulgated its 2004 amendments to the Constitution, adding “the state respects and protects human rights” to it. The Criminal Procedure Law amended in 2012 included “respecting and protecting human rights” in the general provisions. China’s judicial organs are taking effective measures in accordance with the law to deter and prohibit extorting confessions by torture, protect the rights to defense of criminal suspects and defendants, protect attorneys’ rights to exercising their duties, limit the applicable measures of detention to protect the lawful rights of detainees, strengthen the protection of the legal rights and interests of detainees, strengthen the protection of juvenile suspects and defendants, strictly control and prudently apply the death penalty, improve the systems of community rehabilitation for inmates and assistance for persons released after serving their terms, and improve the state compensation system and establish systems including the criminal victim relief system, in an attempt to materialize efforts in human rights protection in the sphere of criminal justice.
1. Prohibiting and Deterring Extortion of Confessions by Torture
To improve the investigation and questioning system is a prerequisite for building the rule of law, and it is also an important method for strengthening judicial supervision and protecting the legal rights and interests of criminal suspects in accordance with the law. China is constantly improving its laws to prohibit the exacting of evidence through torture or other illegal means by judicial officials.
Banning self-incrimination. The Criminal Procedure Law amended in 2012 clearly stipulates that no person may be forced to prove his or her own guilt, and no criminal suspects or defendants may be forced to confess.
Excluding illegally obtained evidence. The Criminal Procedure Law amended in 2012 makes it clear that confessions by a suspect or a defendant obtained through extortion or other illegal means and witness’s testimony and victim’s statements obtained through the use of violence, threats or other illegal means should be excluded from evidence. If physical or documentary evidence is collected in ways violating legal procedures and severely affecting judicial justice, such evidence should be excluded if no correction or justification is provided. It also stipulates the specific procedure for exclusion of such evidence. Once evidence that should be excluded is found by public security organs, people’s procuratorates or people’s courts during the course of investigation, prosecution review or trial, such evidence should be excluded in accordance with the law.
Improving the system of detention, taking a person into custody after arrest, and interrogation. A person who has been detained must be sent to a house of detention within 24 hours. When a person is arrested, he/she must be taken into custody immediately in a house of detention, where the interrogation shall be conducted. With advances in the IT-based law enforcement by judicial organs, interrogation, detention, court trials and activities happening in places of custody are recorded and video taped. The practice of recording and videotaping investigation and questioning processes is widely adopted. The law explicitly states that for crimes punishable by life imprisonment or death and other serious crimes, audio or video recording of the interrogation process is mandatory. The audio or video recording should cover the entire process of the questioning and should be complete.
2. Protecting the Right to Defense of Suspects and Defendants
The system of advocacy set up for implementing the right to defense as stipulated in China’s Constitution is a basic system in China’s criminal litigation. It demonstrates the respect of the state for human rights such as those to life and freedom. In recent years, China has been reforming and improving its system of advocacy, aiming to change the old conception of “stressing fighting crimes, but ignoring human rights protection” in judicial practice, and make the system of advocacy play its due role in human rights protection.
Ensuring timely defense. The Criminal Procedure Law of 1979 stated that a defendant is not entitled to appoint a defender until he/she is undergoing court trial. The amended version in 1996 stipulated that a criminal suspect is entitled to hire an attorney for legal assistance during the investigation period, and appoint a defender when the case is handed over to a prosecution organ when the investigation is concluded. And the newly amended Criminal Procedure Law of 2012 went further to specify that a criminal suspect has the right to appoint a defender at any time as of the date when he/she is interrogated for the first time or from the day on which compulsory measures are adopted against him/her. A defendant is entitled to hire a defender any time he/she wants. If a criminal suspect or defendant in custody requests the appointment of a defender, the people’s court, the people’s procuratorate or the public security organ should convey the message promptly, and a defender may also be appointed by his/her guardian or a close relative on his/her behalf.
Expanding the scope of legal assistance. In order to further protect the rights to defense and other relevant rights of criminal suspects and defendants, the Criminal Procedure Law amended in 2012 expanded the scope of legal assistance in criminal litigation, to make it cover the investigation and prosecution review processes as well as trials, and expanded the scope of people entitled to receive such assistance. If the criminal suspect is blind, deaf or mute, or is a minor or is a mentally ill person who has not completely lost his/her capacity to comprehend or to control his/her behavior, or if a criminal suspect may be sentenced to life imprisonment or death, but he/she has not appointed a defender, the relevant people’s court, people’s procuratorate or public security organ should inform the legal assistance agency to assign a defense attorney.
Stressing witness’s duty to testify in court. Witness testimony in court is crucial to improving the quality of a court trial. In order to have more witnesses testify in court, the Criminal Procedure Law amended in 2012 defines the scope of witness appearance at a court and sets up an assistance mechanism for their appearance at court. It stipulates that if the prosecutor and the defender disagree upon the testimony of a witness that bear significantly on sentencing, the witness should attend the court. A witness should be compensated for transportation, accommodation and meal expenses related to his/her court duties by the government. The employer of the witness may not reduce or reduce in disguise the witness’s remuneration, bonuses or other social benefits in the period he/she is absent from work providing testimony.
Improving protection for witnesses. In cases involving serious crimes, if the personal safety of a witness, expert witness, or victim or a close relative of the same is at risk because of court testimony, the relevant people’s court, people’s procuratorate and public security organ should withhold the personal information, and disguise the appearance and voice of such persons during testimony, prohibit certain persons to be in contact with the witnesses, or their close relatives, and take special measures for personal and residential protection.
3. Protecting Lawyers’ Rights to Practice
The protection of lawyers’ rights to practice in the course of criminal litigation is essential to protecting the lawful rights and interests of the criminal suspect or defendant and ensuring that such cases are dealt with impartially. China is revising related laws to provide a legal guarantee for lawyers to overcome difficulties in meeting with the suspect or defendant, accessing to materials concerning the case and obtaining evidence through investigation.
The Law of the People’s Republic of China on Lawyers, amended in 2007, supplemented and stressed lawyers’ rights in the course of litigation, particularly criminal litigation. It stipulates that the representation or defense opinions presented in court by a lawyer shall not be subject to legal prosecution so long as they do not compromise national security, maliciously defame others or seriously disrupt court order. These measures have effectively promoted the exercise of the defense function of lawyers. From 2006 to 2011, lawyers throughout the country provided defense for a total of 2,454,222 cases, an increase of 54.16% over the period 2001-2005.
A timely meeting with a client in custody, access to case materials and obtaining evidence through investigation bear directly on the practice of the defense attorney in criminal litigation. The Criminal Procedure Law amended in 2012 specifies that, except for few cases, a defense attorney who holds a license for practicing law, a certificate of his law firm and a letter of attorney or an official legal assistance letter may meet a detained suspect or defendant. Such a meeting is not to be monitored. Starting from the date of the review by the people’s procuratorate, a defense attorney may have access to, extract and copy filed materials concerning the case. A defender may apply to the relevant people’s procuratorate or people’s court for evidence of the innocence of the defendant or the insignificance of the alleged crime collected by the public security organ or the people’s procuratorate. It also specifies that if a defender thinks the public security organ, the people’s procuratorate, the people’s court or their staff hinders him/her from exercising his/her litigation right, he/she has the right to make a petition/accusation to a people’s procuratorate at the same level or at the next higher level. The people’s procuratorate must review the petition/accusation in a timely fashion. If the petition/accusation is true, the people’s procuratorate will notify the relevant department to make corrections to its acts.
4. Restrictions on Application of Custody
In order to safeguard public safety and guarantee the smooth conduct of criminal case investigation, Chinese law specifies both custodial and non-custodial measures to be imposed on a criminal suspect or defendant as well as the strict conditions of their application. To further regulate the application of these compulsory measures and strengthen the protection of civil rights, the Criminal Procedure Law amended in 2012 further improves the compulsory custodial measures.
Refining conditions and approval procedures for arrest. The newly revised Criminal Procedure Law clearly defines social risk criteria of offences, stipulating that when a people’s procuratorate reviews and approves an arrest application it may question the suspect. It must question the suspect when it doubts whether the conditions for arrest are met, or the suspect requests to give a statement to the prosecutor face to face, or the investigation may have been in serious violation of the law. If the defense attorney asks to express his opinion, this request should be granted. These provisions help investigators and the investigating authorities get a thorough understanding of the case, and an accurate grasp of the conditions for arrest, thus avoid putting someone in custody by mistake.
Establishing a system of review over the necessity of detention. After a criminal suspect or defendant is arrested, the people’s procuratorate should still check the necessity for detention. If the detention is found to be not necessary, the judicial authorities concerned should be advised to release the detainee or alter the compulsory measures.
Improving the procedures for terminating and altering compulsory measures imposed on detained suspects or defendants. The people’s court, people’s procuratorate or public security organ shall cancel or alter the compulsory measures promptly or release the detained person upon expiration of the statutory period for custody or as soon as they find that the custody measures imposed on a suspect or a defendant are not appropriate. The criminal suspect, defendant, his statutory representative, close relative or defender are entitled to request an alteration of the compulsory measures imposed, and the relevant authority shall respond within three days.
Expanding application of residential surveillance and reducing application of detention. The Criminal Procedure Law revised in 2012 defined residential surveillance as an alternative to detention. It puts under residential surveillance those who meet the conditions for arrest but are seriously ill and unable to take care of themselves, or pregnant women or women currently breastfeeding their own babies, or someone who is the only caregiver of a person who cannot take care of himself/herself.
5. Protecting the Legal Rights and Interests of Detainees
A house of detention is a criminal custody institution for detaining persons who have been arrested and taken into custody in accordance with the law. Protecting detainees’ legal rights and interests not only demonstrates the level of civilized and standardized legal enforcement of the house of detention but is also the need for human rights protection.
China attaches great importance to improving the surveillance level of houses of detention, prohibits extorting confessions by torture and overdue custody, improves the conditions for detention and surveillance, improves the living conditions of detainees and protects their lawful rights and interests. A body surface examination will be conducted on a detainee daily within seven days after he/she is sent to a house of detention, and this examination system is also strictly implemented before and after a round of interrogation, as well as before and after a detainee is sent away from or back to a house of detention. The system of one bed for each inmate will be gradually adopted, and medical care for prison inmates will be socialized, so as to ensure that an inmate gets timely treatment in case of illness. The system of investigation and handling of complaints by detainees will be improved, so will the system of detainees’ meeting with the police, officials of detention houses or resident procurators upon their requests, so as to receive and investigate complaints and accusations by detainees on time. When the term of detention for a detainee is to expire, the house of detention should submit a written report to the resident procurator’s office, which in turn will supervise whether the release of the detainee or alteration of the compulsory measures by the investigation authorities are carried out promptly. From 2008 to 2011, procuratorial organs conducted supervision and examination of houses of detention throughout the country, and corrected 5,473 cases of illegal detention. Efforts are being made to crack down on bullying rogues in prisons, and alarm devices are installed in each cell so that the detainees can call the police on time in case of abuse. The practice is adopted whereby officials talk to detainees upon their release from the house of detention, with follow-up observations and meetings with them for better monitoring over bullying rogues in houses of detention. A responsible system is implemented for chief and assistant policemen in management of prison cells, and those concerned shall be held accountable if there are serious injuries or deaths of detainees inflicted by bullies because of lax management. The system of inviting special supervisors to inspect detention facilities will be established whereby invited special supervisors may come and inspect the performance of duties and law enforcement by the police in the houses of detention during working hours without notification in advance. In 2010, the number of accidents in houses of detention fell by 31.6% compared with 2009. Video meetings with detainees is being introduced in houses of detention across the country to facilitate family visits. The systems of security risk assessment and separate management of detainees have been established, and psychological intervention has been strengthened for detainees. The working principle of “education, persuasion and rehabilitation,” which integrates educational measures with management and care for detainees, is upheld in order to help them foster again a positive attitude towards life and healthy lifestyle.
6. Protecting the Legal Rights and Interests of Juvenile Suspects and Offenders
China adopts the measure of combined punishment and protection to help juvenile offenders and does the utmost to rehabilitate them and get them reintegrated into society. China specifies the principle of “education, persuasion and rehabilitation” for juvenile offenders, sticking to the principle of applying primarily educational measures, and taking punitive sanctions as ancillary means. The judicial organs assign officials who have a good knowledge of the physical and psychological characteristics of minors to handle juvenile cases. If a minor defendant has not appointed a defender, the judicial organs should notify a legal assistance agency to assign an attorney to defend him/her. There are strict rules regarding the arrest of a juvenile suspect or defendant. When a people’s prosecutor’s office reviews and approves an arrest and a people’s court decides on the arrest of a minor, the minor shall be questioned and the defense attorney’s opinion shall be heeded. Minors held in custody, arrested or are under criminal punishment shall be detained, administered and educated separately from adults. During the interrogation and trial of juvenile criminal cases, the legal representative of the minor should be present. The court may also inform the minor’s other adult relatives or representatives of his/her school, work unit, place of residence or juvenile protection organizations of the trial so that they shall be present. If the legal representative or any other relevant person present believes that the legitimate rights and interests of the minor have been infringed upon during the interrogation or trial, he/she may express his/her opinion thereon. The interrogation or court records shall be made available on the spot to the legal representative or other relevant person present to read or be read out to them. When female juvenile suspects are interrogated, a female officer shall be present. For a minor whose offence is not serious, therefore may be sentenced to less than one year in prison but who has shown remorse, the people’s procuratorate may decide not to proceed with prosecution, with conditions attached. The judicial organs may take into consideration the family and school background, cause of crime, guardianship and education of a juvenile offender and use them as reference when handling the case. Trial of cases in which the offenders are under the age of 18 shall not be open to the public. If the offender is under 18 at the time of the crime and sentenced to less than five years of imprisonment, the records of the crime shall be sealed. These records shall not be disclosed to any institution or individual unless they are required by judicial authorities for handling cases or by relevant institutions for inquiry in accordance with state regulations. Amendment Eight to the Criminal Law promulgated in 2011 makes clear the conditions under which probation is applicable to a minor. It also stipulates that juvenile offenders do not constitute recidivists. By July 2011, a total of 2,331 juvenile courts had been set up across the country. From 2002 to 2011, thanks to efforts from all sectors of society, the rate of recidivism of China’s juveniles remained at 1% to 2%. In recent years, cases of juvenile delinquency have been falling, and the proportion of juvenile offenders among the criminal population is gradually decreasing.
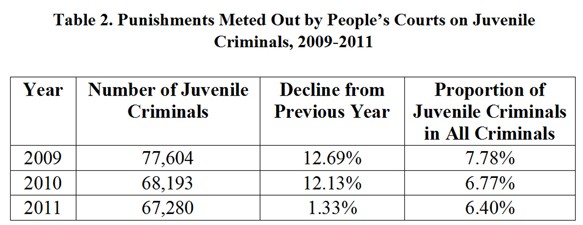
The graphics shows punishments meted out by people's courts on juvenile criminals from 2009 to 2011, according to China's white paper on judicial reform published by the Information Office of the State Council on Oct. 9, 2012.
7. Strict Control over and Prudent Application of the Death Penalty
China retains the death penalty, but strictly controls and prudently applies it. China’s Criminal Law stipulates that the death penalty shall only be applied to criminals who have committed extremely serious crimes, and has very strict stipulations on its application. Amendment Eight to the Criminal Law promulgated in 2011 eliminated the death penalty for 13 economy-related non-violent offences, accounting for 19.1% of the total death penalty charges. It stipulates that death penalty shall generally not be used for people who are already 75 years old at the time of trial. It also established the system of death penalty with a suspension of execution and put restrictions on reduction of sentences. These are attempts to create conditions in legislation and system to gradually reduce the use of the death penalty.
The death penalty bears directly on the citizen’s right to life, so it must be applied in a very prudent manner. Starting in 2007, only the Supreme People’s Court has the right to approve death penalty. In China, court trials of all death penalty cases of the second instance are open to the public. The state has improved the death penalty review procedure and strengthened supervision over the death penalty review. When the Supreme People’s Court reviews a death sentence, it shall question the defendant, and hear the opinion of the defense attorney if the attorney makes the request. During the review of a death sentence, the Supreme People’s Procuratorate may advise the Supreme People’s Court of its opinions. The reform of the death penalty review procedure guarantees fairness in handling death penalty cases. Since 2007, when the Supreme People’s Court began to exercise the right to review death sentences, the standard for the application of the death penalty has been more uniform and the number of death sentences in China has dropped gradually.
8. Improving Community Correction System for Persons Serving Sentences and Assistance System for Persons Released from Prison
Improving law-enforcement conditions of prisons and results of education and reform. China is striving to build a just, clean, civilized and efficient prison system, realizing its reform objective of “full-sum guarantee, separation of administrative and business functions, separation of revenues and expenditures, and standardized operation” of prisons. The expenses for jail administration, criminal reformation, prisoners’ cost of living, and jail facilities are all guaranteed by the government budget. Inmates are required to work in prison and get paid. Every week, they work for five days, receive classroom education for one day and rest for one day. Attempts are made to strengthen moral, cultural, and technical education to inmates and give them vocational training so as to enhance their ability to make a living after being released. Since 2008, a total of 1.26 million inmates have completed literacy and other compulsory education courses while serving their sentences, and over 5,800 people have acquired college diplomas recognized by the state. Over 30,000 skill-training courses of various kinds have so far been conducted by prisons across the country, and over 75% of inmate trainees have received related certificates, made about 14,000 technological innovations and obtained over 500 invention patents.
Carrying out community correction. In recent years, China has committed itself to reforming and improving the punishment system. It launched this effort in 2003 to introduce community correction experiments first, and then spread it across the country in 2009, putting criminals who have been under surveillance, received a suspended sentence, been released on parole or temporarily served a sentence outside prison into community correction organizations. The aim of this is to correct their crime-prone mentality and harmful behavior with the assistance of social forces and help them reintegrate into society. Community correction has been established as a legal system by China’s Criminal Law and Criminal Procedure Law. By June 2012, a total of 1.054 million people had received community correction, and 587,000 people had been released from such correction. The recidivism rate of those undergoing community correction is around 0.2%.
Improving the system of assistance to people released from prison. The Chinese government pays great attention to helping solve difficulties encountered by people released from prison in life and employment. Those who are eligible for the minimum subsistence allowance are covered by this system. Others who face economic difficulties but ineligible for the minimum subsistence allowance are given temporary assistance. People released from prison who are starting their own businesses and enterprises providing jobs for them can enjoy tax breaks and reduction of administrative fees. According to available statistics, people who are released from prison and receive social assistance across the country increased 2.7-fold from 2008 to 2011. The recidivism rate of such people remains low.
9. Improving the State Compensation System
China has established a state compensation system to compensate citizens, legal persons or other organizations if their lawful rights and interests are damaged by state organs or their functionaries in the course of enforcing their power in accordance with the law. The State Compensation Law of the People’s Republic of China amended in 2010 sets up necessary offices responsible for state compensation, opens up the channels for claiming compensation, expands the compensation scope, specifies the burden of proof, adds compensation for psychological injury, increases the compensation standards, and guarantees the timely payment of compensation. This has further improved the system of administrative compensation, criminal compensation, and non-criminal judicial compensation. In recent years, the standard of state criminal compensation has been rising along with social and economic development. The daily payment for infringement upon a citizen’s right to freedom was increased from 17.16 yuan in 1995 to 162.65 yuan in 2012. In 2011, a total of 6,786 cases concerning administrative compensation (first instance), criminal compensation and non-criminal judicial compensation were concluded by people’s courts at all levels. Among them, 868 were criminal compensation cases, with the aggregate amount of compensation standing at 30.67 million yuan, representing increases of 16.04% and 42.9% respectively as compared with 2009.
10. Establishment of Assistance System for Crime Victims
In recent years, China has been actively exploring ways to establish an assistance system for crime victims. The government will provide appropriate financial support to crime victims who are not able to get effective and timely compensation, live in poverty and particularly to those violent crime victims who are severely injured, disabled or dead or to their immediate family members. The assistance standard and scope for crime victims shall be set in the light of the local economic and social conditions. The crime victim assistance work should be done in combination with related measures, such as legal assistance, judicial assistance and social security, improving the guarantee system for the rights and interests of crime victims. From 2009 to 2011, the judicial authorities issued assistance funds worth a total of 350 million yuan to 25,996 crime victims, and provided legal assistance in 11,593 cases.
IV. Enhancing Judicial Capabilities
Improving judicial capabilities is an important goal of China’s judicial reform. In recent years, China has continuously improved its qualification system for the legal profession, strengthened occupational and ethical training, and improved its funding guarantee, thus effectively improving judicial capabilities and laying a solid foundation for enhancing the public credibility of the judiciary.
Implementing a unified national judicial examination system. China has established and constantly improved its national judicial examination system by incorporating qualification examinations for junior judges, junior prosecutors, lawyers and notaries. The national judicial examination system for access to the legal profession plays an important role in regulating qualifications for legal personnel, improving the overall quality of judicial staff and promoting the professionalism of legal personnel. Since 2002, the national judicial examination has been held annually. Organized and implemented nationwide, it has evolved into a unified system for access to the legal profession. By the end of 2011, nearly 500,000 people had passed the national judicial examination and were qualified to work in the field of law.
Establishing a tiered law-enforcement qualification examination system for the police. To enhance the capabilities of its police officers, China requires all on-the-roster police officers in public security organs to take a qualification examination on law enforcement. Those who fail shall not be entitled to enforce the law. In 2011, the examination was taken by a total of 1.73 million police officers, of whom over 1.69 million passed.
Strengthening occupational training for judicial staff. To keep up with the times and meet the public’s increasing demands on the judiciary, China pays increasing attention to improving the occupational training system for judicial staff and elevating their capabilities. The central and provincial-level judicial organs have now established training agencies, formulated training plans, and extended training for all judicial staff, while setting up various specific training systems, including required training for junior officials and officials prior to promotion. The training programs have changed the traditional mode that focused on higher academic degrees and theoretical knowledge, but selected judges, prosecutors and police officers who have rich practical experience and a relatively high level of theoretical knowledge to serve as teachers. This educational training is designed to tackle the key, difficult points and newly emerging conditions and problems, and constantly improve practicability. Over the past five years, China has trained some 1.5 million judges, 750,000 prosecutors and 6 million police officers.
Intensifying professional ethical training for judicial staff. In light of different features of their work, judicial organs have formulated basic work ethics, setting forth specific requirements for judicial staff in such aspects as moral values, conduct in performing duties, discipline, style and etiquette in work, and conduct off duty. In 2011, a campaign for spreading core values was launched among China’s judicial staff, taking “loyalty, for the people, justice and incorruptibility” as the common values to be held by them.
Strengthening professional ethics training for lawyers. This training, which highlights “always following the law, observing good faith, working diligently, and ensuring justice,” is being carried out to build up the professional ethics of lawyers. Attempts are made to consolidate the self-discipline of the lawyers association, to establish a credibility system for practicing lawyers, and to improve the mechanism for evaluating and supervising the credibility of practicing lawyers and for punishing dishonest practicing lawyers so as to spur lawyers to increase their sense of responsibility in safeguarding the lawful rights and interests of the recipients of their services, to guarantee proper enforcement of the law, and to uphold equity and justice and ultimately to improve the moral standards and credibility of lawyers.
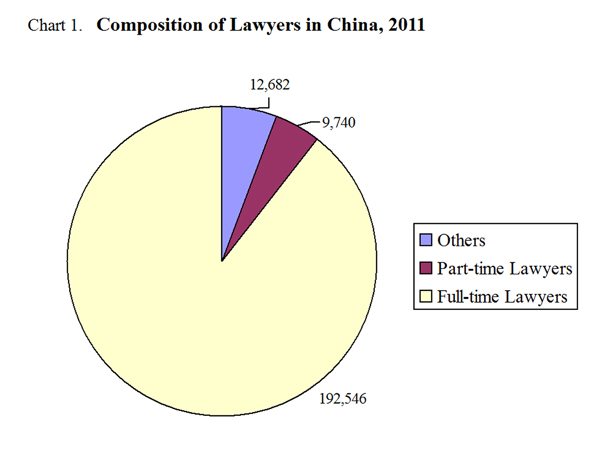
The graphics shows composition of lawyers in China in 2011, according to China's white paper on judicial reform published by the Information Office of the State Council on Oct 9, 2012.
Expanding space in which lawyers play their role. China has borrowed international experience in establishing the systems of public defenders and corporate lawyers. Since 2002, the country has trial-established the systems to provide legal counsel for government decision-making and major corporate operations, thus improving the structure of the law business that is composed of public defenders, corporate lawyers as well as lawyers in the common sense (including full-time and part-time ones). The Lawyers Law, revised in 2007, improves the organizational form of law firms, allowing individuals to open law firms. Thus, a setup of state-funded, partnership and individually owned law firms has been established. By the end of 2011, China had had 18,200 law firms, an increase of 31.6% compared with 2008. Among them, 13,500 were partnerships, 1,325 state-funded ones and 3,369 individually owned ones. There had been more than 210,000 lawyers, of whom full-time lawyers accounted for 89.6%, part-time ones made up 4.5%, while the rest were corporate lawyers, public defenders, legal-assistance lawyers and military lawyers. In 2011, China’s lawyers acted as legal counselors for 392,000 clients, an increase of 24.6% compared with 2008; they handled 2.315 million litigation cases, 625,000 non-litigation cases and 845,000 legal-assistance cases, up by 17.7%, 17% and 54.5% respectively as compared with 2008.

The graphics shows cases undertaken by lawyers from 2008 to 2011, according to China's white paper on judicial reform published by the Information Office of the State Council on Oct 9, 2012.
Reforming the funding guarantee system for judicial organs. China initiated a new round of judicial reform in 2008, clearly proposing that a funding guarantee system for judicial organs will be established, featuring “funding by category, separate management of income and expenditure, and full-sum coverage.” The central and provincial governments have increased their funding for judicial organs, ensuring full-sum coverage for the expenses of judicial organs at all levels, resulting in great improvement in the performance capacity of grassroots judicial organs. Litigation fees collected by judicial organs in accordance with the law and revenues from fines and confiscations are all turned over to the national treasury to ensure the separation between income and expenditure as well as between penalty decisions and penalty payments, so as to halt wanton collection of fees and fines that are driven by the hunger for economic gains. The state has also formulated standards for the construction of basic facilities and equipment for judicial organs to improve their working conditions and information and technological levels, providing concrete guarantees for enhancing judicial capabilities.
V. Judicial Power Serving the People
Putting the people first and exercising judicial power for the people are the fundamental starting point and ultimate objective of judicial work in China. In recent years, in light of new situations and requirements coming along with the rapid socioeconomic development, China has made continuous efforts in promoting the development of the grassroots judicial organs by intensifying service consciousness in judicial work, extending work platforms and improving work procedures, so as to provide more convenience for people to exercise their rights.
1. Strengthening the Development of Grassroots Judicial Organs
Most of the cases handled by the judicial bodies take place at grassroots level, and grassroots judicial institutions are the frontline platforms providing judicial services to the public. The local grassroots courts, procuratorates, public security organs and judicial administrative bodies are strengthening such agencies as people’s tribunals, procuratorial offices, police stations and judicial offices to make judicial services close to the people and provide better service to them.
Strengthening the construction of grassroots people’s courts. Every year grassroots people’s tribunals try an average of 2.4 million cases, accounting for one-third of all cases tried by the people’s courts of first instance across the country. In recent years, to facilitate litigation, local grassroots people’s courts have resumed, built or improved the people’s tribunals, and promoted a mechanism for people’s tribunals to directly place cases on file for investigation by simplifying this procedure. Currently, China has nearly 10,000 people’s tribunals, covering almost all towns or townships and urban neighborhoods. Convenient litigation offices and liaison points have been set up in remote villages and litigation liaisons are appointed. Circuit tribunals have been set up in places where there is relative concentration of population, and they are encouraged to receive and hear cases as they go the rounds so as to serve the people as best they can.
Strengthening the construction of grassroots procuratorial offices. Local grassroots people’s procuratorates have established sub-offices in some major townships or towns to receive reports from the masses about offences, their complaints and petitions, to find clues to crimes involving government functionaries, to exercise legal supervision over illegal practices in litigation, to do publicity work on crime prevention and the rule of law, to participate in social security comprehensive management and safety building, and to supervise and coordinate with community correction work. So far, China’s procuratorates have set up 2,758 such offices, and 9,622 other procuratorial agencies like liaison stations and work stations.
Strengthening the construction of grassroots police stations. Public security organs are promoting a community policing strategy in urban and rural areas. Now China has more than 50,000 police stations and over 170,000 sub-stations, covering all the townships, towns and neighborhoods, making police services and distribution of police forces closer to the grassroots and the public. Public security organs have remarkably improved their capabilities to prevent and crack down on crimes, control security situation and serve the people. Since 2006, cases of serious violent crimes in eight categories handled by public security organs nationwide, including murder, robbery, rape, kidnapping and personal injury, have kept going down, by 9% in 2010 from 2009, and by 10% in 2011 from 2010.
Strengthening the construction of grassroots judicial offices. In recent years, in addition to the functions of legal publicity, legal assistance, mediation guidance and grassroots legal services, the grassroots judicial offices have taken upon themselves such new functions as community correction, and settling down and rehabilitating those committing minor offences. Currently, China has more than 40,000 such offices, covering most of the country’s townships or towns and urban districts. In the 2004-2011 period, the judicial offices solved 2.84 million disputes, assisted in the mediation and settlement of 46.77 million difficult and complex disputes, participated in resettlement of 2.69 million ex-convicts, and guided the handling of 1.12 million legal-assistance cases.
2. Simplifying Case-Handling Procedures
Recent years have seen a sharp rise in litigation cases. On the basis of giving comprehensive consideration to the nature and complexity of the cases, the people’s courts classified the cases into complex ones and simple ones and adopted different hearing procedures for different cases, thus applying different hearing procedures to cases of different natures to optimize judicial resources and enhance litigation efficiency.
Extending the scope of application of the summary procedures for criminal cases. The Criminal Procedure Law amended in 2012 extends the scope of application of the summary procedures from cases punishable by no more than three years in jail to all criminal cases under the jurisdiction of grassroots people’s courts.
Promoting the reform of small-claim litigation. To safeguard the legitimate rights and interests of the parties concerned promptly and fairly, small-claim litigations are heard using simple procedures on a trial basis in some grassroots people’s courts. If both parties involved agree to use simple procedures, when the people’s court hears a civil case in which the facts, rights and obligations are clear, and involves a small sum of money, the trial of first instance will be final. Based on the previous experiences, the Civil Procedure Law amended in 2012 stipulates that among the simple civil cases heard by the grassroots people’s courts, if the sum of money involved is less than 30% of the annual average wage of employees in the previous year in the province (autonomous region or municipality directly under the central government) in question, then the trial of first instance will be final. This legislation affirms the reform of small-claim litigation.
Summary procedure for administrative cases. For an administrative case of first instance in which the basic facts are evident and the dispute is trivial in character, involving a small amount of property, the people’s court may, on the premise of mutual agreement between the parties concerned, have a single judge try the case, simplify the litigation procedures, and conclude the case within 45 days after it is placed on the docket.
3. Establishing Multiple Dispute Resolution Mechanisms
In response to the frequently occurring conflicts and disputes in a period of rapid social development, in 2010 the legislative organ of China promulgated the Law of the People’s Republic of China on Mediation, and relevant department issued Several Opinions on Establishing and Improving Conflict and Dispute Resolution Mechanisms by Linking Litigation and Non-litigation Cases and Guidelines on Encouraging the Use of Mediation to Solve Conflicts and Disputes. They encourage the development and improvement of non-litigation dispute resolution mechanisms, thus establishing multiple dispute resolution mechanisms suited to the national conditions. Provisions such as mediation should be used first and mediation agreements shall be accepted by judicial organs are added to the Civil Procedure Law amended in 2012, reaffirming the achievements in judicial reforms.
Giving play to people’s mediation. People’s mediation is a Chinese way for resolving non-litigation disputes. China has established people’s mediation committees in village (neighborhood) committees, townships or towns (urban districts), enterprises and public institutions, as well as industries and sectors with a high frequency of occurrence of disputes. By the end of 2011, China had 811,000 people’s mediation organizations and 4.336 million mediators. In 2011, a total of 8.935 million conflicts were resolved through mediation, with a 96.9% resolution rate.
Giving play to administrative mediation. Out of the volition of the parties involved, an administrative organ may mediate administrative disputes under its jurisdiction and civil disputes relating to its functions and powers, enabling the parties concerned to reach agreement through consultation on an equal footing. Such mediation is conducive to the timely and reasonable settlement of disputes.
Giving play to judicial mediation. A people’s court shall, according to its functions and powers or at the request of the involved parties, mediate civil cases lodged to it and resolve disputes under the presiding of a judge. In 2011, the people’s courts in China mediated 2.665 million civil cases and had 1.746 million cases withdrawn by the parties after mediation. The people’s procuratorates have established and improved a mechanism to link prosecution with mediation. With respect to a minor criminal case or a civil appeal that meets certain requirements, a people’s procuratorate will ask a people’s mediation organization to mediate first before it makes a decision in accordance with the law on the basis of the mediation result to jointly resolve the conflict or dispute.
Strengthening conflict or dispute resolution mechanisms by linking litigation and non-litigation cases. Highlighting the role of people’s mediation organizations, social groups, lawyers, experts and arbitration agencies, China endeavors to establish a “large mediation” work system that integrates people’s, administrative and judicial mediation, and improves coordination among the three in terms of procedure linkage, validity confirmation and legal guidance. As for non-litigation dispute resolution mechanisms like arbitration, the people’s courts respect their own rules and provide support in such aspects as evidence and property preservation, and compulsory execution.
Improving litigation procedures for cases of public prosecution involving conciliation between the parties. For some minor crimes arising from civil disputes and for negligent crimes (excluding dereliction of duty) that may be given sentences of less than seven years, when criminal suspects or defendants repent of their crimes and obtain the forgiveness of the victims through such means as compensation for losses or apologies, and the victims wish to be reconciled with the perpetrators on a voluntary basis, both parties may be reconciled. For cases in which the parties concerned reach conciliation agreements, the people’s procuratorate may recommend lenient penalties to the people’s courts; and for minor crimes that do not entail criminal punishment, the people’s procuratorate may issue non-litigation decisions. The people’s courts may give a lenient penalty to defendants in accordance with the law.
4. Reducing Litigation Costs for Parties Concerned
China has expedited the reform and improvement of its litigation fee collection system. In 2006, China promulgated the Rules on Litigation Fee Payment, and the Methods for Management of Collection of Lawyer Service Fees. These measures markedly lowered the cost of litigants, thus mitigating the difficulty of lodging a lawsuit and hiring a lawyer, while guaranteeing normal judicial work and preventing abuse of litigation rights.
Lowering litigation charges. China has clarified the payment scope concerning litigation fees, with people’s courts collecting only fees for case registration and application. China has sharply adjusted the threshold, percentage and standard of fees for cases involving property, divorce and labor disputes whose occurrence is fairly frequent, resulting in a great reduction in actual charges. Case registration fees are exempted for such cases as administrative compensation. For administrative cases, whether involving property or not, a fixed fee is collected.
Reducing and exempting litigation fees. When a party has difficulty paying a litigation fee it may apply to a people’s court for judicial assistance. The state makes clear the circumstances, procedures and percentages for exemption, reduction and deferment of litigation fees, ensuring that parties with economic difficulties are able to fully exercise their litigation rights in accordance with the law.
Regulating lawyers’ charges. While expanding the scope of lawyers’ charges to market-adjusted prices, China continues to implement government-guided prices for service fees collected by lawyers when they act as representatives in state compensation cases and other law-suits, and rigorously standardizes the links and procedures for lawyers’ charges. This effectively guarantees litigants’ lawful rights and interests, as well as the state’s interests while promoting the healthy development of the law profession.
Facilitating litigation. Judicial organs have generally established litigation service centers, and case registration and reception centers, and initiated and improved such systems as first inquiry responsibility, service commitment, open work and polite reception. They have improved such services as litigation guidance, search and inquiry, mediation prior to litigation, and meeting with people who report offences. They provide a suitable litigation environment for the public by opening hotlines and making use of information technology to provide online services such as case registration, serving a document, court sessions and inquiries.
5. Providing Legal Assistance
China attaches great importance to legal assistance. Since the implementation of the Regulations on Legal Assistance promulgated in 2003, China has gradually extended its coverage of legal assistance, and established and improved its funding guarantee system, providing free legal services for citizens with economic difficulties and parties to special cases of lawsuits, making it possible for more and more impoverished people to protect their legitimate rights and interests through legal assistance. In recent years, legal assistance has extended from criminal defence to areas involving people’s livelihood, such as seeing a doctor, seeking employment and obtaining education; the standards of economic difficulty have been established in reference to local subsistence allowance standards; the subsidies for handling cases have been improved; and specific funding guarantee systems have been established for five special groups: migrant workers, the disabled, the elderly, minors and women. By the end of 2011, China had more than 3,600 legal-assistance agencies, 14,000 full-time legal-assistance personnel, 215,000 lawyers and 73,000 grassroots legal service personnel. A total of 28 provinces (autonomous regions and municipalities directly under the central government) have formulated local statutory regulations on legal assistance. Since 2009, funding for legal assistance has increased at an annual rate of 26.8%, reaching 1.28 billion yuan in 2011. The work of legal assistance has constantly improved along with socioeconomic advances.
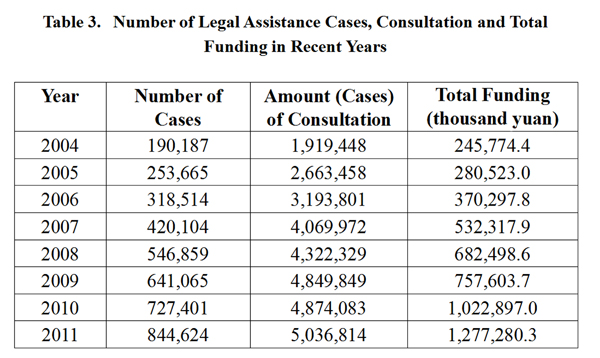
The graphics shows the number of legal assistance cases, consultation and total funding in recent years, according to China's white paper on judicial reform published by the Information Office of the State Council on Oct. 9, 2012.
6. Facilitating Channels of Communication between Judicial Organs and the Public
Judicial organs in China attach great importance to listening to the public’s opinions, and make proactive efforts to guarantee the people’s rights to know, participate in, be heard and supervise in terms of judicial affairs. They have established special departments to strengthen communication with members of the people’s congresses and members of the Chinese People’s Political Consultative Conference, and handle proposals and recommendations related to judicial work. They invite members of the democratic parties, personages without party affiliation and representatives from among the general public to act as special supervisors and procurators, people’s supervisors, and specially-invited consultants to oversee their work and provide comments and advice. They have built websites and microblogs to establish mechanisms for the online expression of public opinion and opinion polls, so as to facilitate communication with the general public. They also approach the public through such activities as receiving visitors, handling petitions and hosting open days.
Conclusion
Through judicial reform, China has constantly improved the socialist judicial system with Chinese characteristics, enhancing rigorous, just, polite and incorruptible law enforcement by the country’s judicial organs, promoting the country’s scientific development of judicial work and personnel, and winning the public’s approval and support.
As circumstances keep changing, there is no end to innovation. Judicial reform is regarded as an important part of China’s political system reform; it is the self-improvement and development of a socialist judicial system with Chinese characteristics. It remains a long and arduous task, and we will deepen the reform along with economic and social development. Establishing a just, effective and authoritative socialist judicial system with Chinese characteristics is the goal of our reform, and China will make continuous efforts to achieve this goal.







